Staging API
In LEXIS, the orchestrator managing the workflows triggers data movement between the different components of the LEXIS Data Infrastructure. That includes moving and deleting input, intermediate files, and output. For this purpose, the Staging API was created. Whole service contains two applications: Staging API and Staging Worker.
Staging API is implemented as a FastAPI application. It provides endpoints for synchronous methods like listing the content of the dataset or requesting asynchronous operations such as staging (data transfer between locations) or data deletion. Each of these asynchronous operations is handled by a Staging Worker. Each centre connected to the LEXIS Platform deploys its own worker. This worker then manages local HPC connections, iRODS zone, or cloud resources.
This communication between the Staging API and the Staging Worker is done through a Distributed Task Queue, which allows to execute long-running tasks. Once a request is triggered on the Staging API, a data management task is pushed to the queue. For each task, we create a unique Request ID, which can be used to track the status of the request via the API.
For the Task Queue, the Celery framework (https://docs.celeryq.dev/en/stable/index.html) was chosen. This framework allows to create a distributed network of workers, where each worker is connected to the central broker (in our case it’s Redis), and a database, where the information about individual tasks is stored. On top of that, each worker can listen on a specific queue. With this approach, we can easily distinguish workers from various data centres and by deploying multiple workers, we can easily scale according to the centre’s requirements.
Image below shows the example of situation that can take place in the platform. Each worker connected to the central broker listens on its own queue. That means the Staging API can easily submit tasks to the worker in the specific centre.
Data movement
One of the main functionalities of the Staging API is data movement. This is used in the workflows to prepare data for the job or to move output data from the cluster to the iRODS. The movement is done by corresponding Staging Worker.
When the request for data movement comes to the Staging API, it dynamically creates a task chain based on the location graph. Each task represents a movement between two locations. This chain is pushed to the queue where each task is processed by a specific worker.
Result of the movement can be tracked by the Request ID.
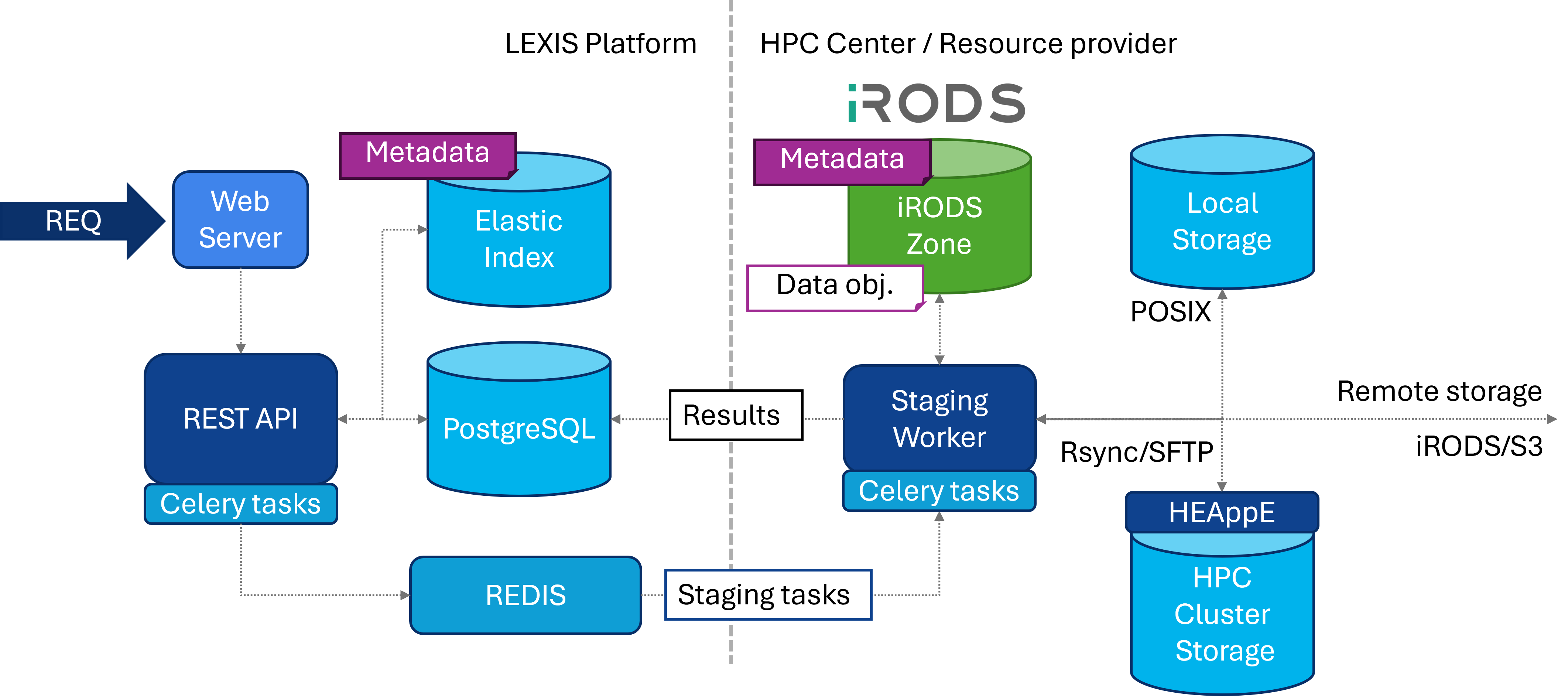
Communication in the DDI
In the image below we see schema of the communication in the DDI.
Source code
The source code and endpoint documentation for the Staging API is available at: https://opencode.it4i.eu/lexis-platform/data/api-v2.
Swagger documentation can be found at: https://api.lexis.tech/api/ddiapi/v2/staging/docs